- Python Slots Vs Data Class
- Monty Python Slot Machine App
- Slot Machine In Python
- Python 3 Class Slots
- Python Slot Machine Code
Released:
A multi-armed bandit library for Python

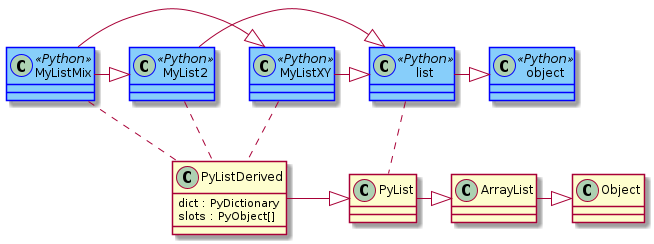
当一个类需要创建大量实例时,可以通过`slots`声明实例所需要的属性, 例如,`class Foo(object): slots = 'foo'`。 这样做带来以下优点: Pythonslots详解 - rainfd - 博客园. Just for completeness of my notes, note that there is a one-time cost per slot in the class's namespace of 64 bytes in Python 2, and 72 bytes in Python 3, because slots use data descriptors like properties, called 'members'. Foo.foo type(Foo.foo) class 'memberdescriptor' getsizeof(Foo.foo) 72.
Project description
A multi-armed bandit library for Python
Slots is intended to be a basic, very easy-to-use multi-armed bandit library for Python.
Author
Roy Keyes -- roy.coding@gmail
License: MIT
See LICENSE.txt
Introduction
slots is a Python library designed to allow the user to explore and use simple multi-armed bandit (MAB) strategies. The basic concept behind the multi-armed bandit problem is that you are faced with n choices (e.g. slot machines, medicines, or UI/UX designs), each of which results in a 'win' with some unknown probability. Multi-armed bandit strategies are designed to let you quickly determine which choice will yield the highest result over time, while reducing the number of tests (or arm pulls) needed to make this determination. Typically, MAB strategies attempt to strike a balance between 'exploration', testing different arms in order to find the best, and 'exploitation', using the best known choice. There are many variation of this problem, see here for more background.
slots provides a hopefully simple API to allow you to explore, test, and use these strategies. Basic usage looks like this:
Using slots to determine the best of 3 variations on a live website.
Make the first choice randomly, record responses, and input reward 2 was chosen. Run online trial (input most recent result) until test criteria is met.
The response of mab.online_trial() is a dict of the form:
Where:
- If the criterion is met,
new_trial=False. choiceis the current choice of arm to try.bestis the current best estimate of the highest payout arm.
To test strategies on arms with pre-set probabilities:
To inspect the results and compare the estimated win probabilities versus the true win probabilities:
By default, slots uses the epsilon greedy strategy. Besides epsilon greedy, the softmax, upper confidence bound (UCB1), and Bayesian bandit strategies are also implemented.
Regret analysis
A common metric used to evaluate the relative success of a MAB strategy is 'regret'. This reflects that fraction of payouts (wins) that have been lost by using the sequence of pulls versus the currently best known arm. The current regret value can be calculated by calling the mab.regret() method.
For example, the regret curves for several different MAB strategies can be generated as follows:
API documentation
For documentation on the slots API, see slots-docs.md.
Python Slots Vs Data Class
Todo list
- More MAB strategies
- Argument to save regret values after each trial in an array.
- TESTS!
Contributing
I welcome contributions, though the pace of development is highly variable. Please file issues and submit pull requests as makes sense.
The current development environment uses:
- pytest >= 5.3 (5.3.2)
- black >= 19.1 (19.10b0)
- mypy = 0.761
You can pip install these easily by including dev-requirements.txt.
For mypy config, see mypy.ini. For black config, see pyproject.toml.
Release historyRelease notifications | RSS feed
Monty Python Slot Machine App
0.4.0
Slot Machine In Python

0.3.1
0.3.0
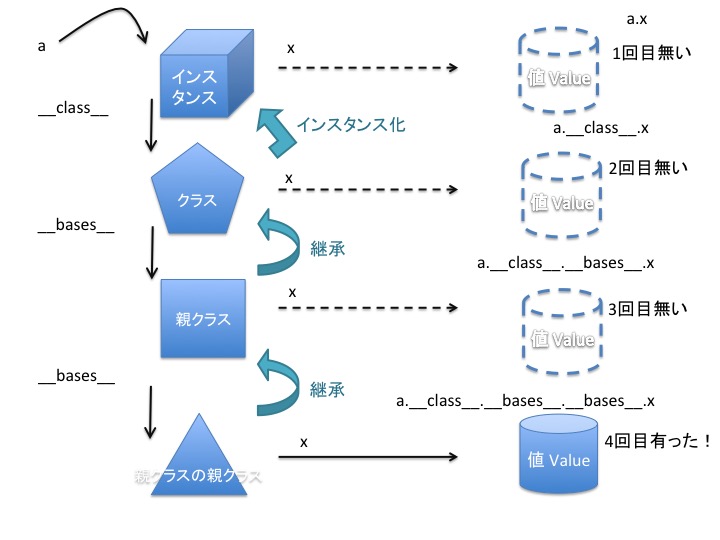
当一个类需要创建大量实例时,可以通过`slots`声明实例所需要的属性, 例如,`class Foo(object): slots = 'foo'`。 这样做带来以下优点: Pythonslots详解 - rainfd - 博客园. Just for completeness of my notes, note that there is a one-time cost per slot in the class's namespace of 64 bytes in Python 2, and 72 bytes in Python 3, because slots use data descriptors like properties, called 'members'. Foo.foo type(Foo.foo) class 'memberdescriptor' getsizeof(Foo.foo) 72.
Project description
A multi-armed bandit library for Python
Slots is intended to be a basic, very easy-to-use multi-armed bandit library for Python.
Author
Roy Keyes -- roy.coding@gmail
License: MIT
See LICENSE.txt
Introduction
slots is a Python library designed to allow the user to explore and use simple multi-armed bandit (MAB) strategies. The basic concept behind the multi-armed bandit problem is that you are faced with n choices (e.g. slot machines, medicines, or UI/UX designs), each of which results in a 'win' with some unknown probability. Multi-armed bandit strategies are designed to let you quickly determine which choice will yield the highest result over time, while reducing the number of tests (or arm pulls) needed to make this determination. Typically, MAB strategies attempt to strike a balance between 'exploration', testing different arms in order to find the best, and 'exploitation', using the best known choice. There are many variation of this problem, see here for more background.
slots provides a hopefully simple API to allow you to explore, test, and use these strategies. Basic usage looks like this:
Using slots to determine the best of 3 variations on a live website.
Make the first choice randomly, record responses, and input reward 2 was chosen. Run online trial (input most recent result) until test criteria is met.
The response of mab.online_trial() is a dict of the form:
Where:
- If the criterion is met,
new_trial=False. choiceis the current choice of arm to try.bestis the current best estimate of the highest payout arm.
To test strategies on arms with pre-set probabilities:
To inspect the results and compare the estimated win probabilities versus the true win probabilities:
By default, slots uses the epsilon greedy strategy. Besides epsilon greedy, the softmax, upper confidence bound (UCB1), and Bayesian bandit strategies are also implemented.
Regret analysis
A common metric used to evaluate the relative success of a MAB strategy is 'regret'. This reflects that fraction of payouts (wins) that have been lost by using the sequence of pulls versus the currently best known arm. The current regret value can be calculated by calling the mab.regret() method.
For example, the regret curves for several different MAB strategies can be generated as follows:
API documentation
For documentation on the slots API, see slots-docs.md.
Python Slots Vs Data Class
Todo list
- More MAB strategies
- Argument to save regret values after each trial in an array.
- TESTS!
Contributing
I welcome contributions, though the pace of development is highly variable. Please file issues and submit pull requests as makes sense.
The current development environment uses:
- pytest >= 5.3 (5.3.2)
- black >= 19.1 (19.10b0)
- mypy = 0.761
You can pip install these easily by including dev-requirements.txt.
For mypy config, see mypy.ini. For black config, see pyproject.toml.
Release historyRelease notifications | RSS feed
Monty Python Slot Machine App
0.4.0
Slot Machine In Python
0.3.1
0.3.0
0.2.0
0.1.0
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
| Filename, size | File type | Python version | Upload date | Hashes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filename, size slots-0.4.0-py3-none-any.whl (8.7 kB) | File type Wheel | Python version py3 | Upload date | Hashes |
| Filename, size slots-0.4.0.tar.gz (174.8 kB) | File type Source | Python version None | Upload date | Hashes |
Hashes for slots-0.4.0-py3-none-any.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest |
|---|---|
| SHA256 | 2bc3e51a6223ae3984476f5d1bb272e70ca6d74fbd298fe48c7283cc1c358cc7 |
| MD5 | 1ec6d4398f2a36036f452a9c77d0d43c |
| BLAKE2-256 | 61dacfca624262fdcce7c043b5e96f06a64019d4a6581a31d5e34ee52b9d30cd |
Python 3 Class Slots
Hashes for slots-0.4.0.tar.gz
Python Slot Machine Code
| Algorithm | Hash digest |
|---|---|
| SHA256 | b02b7b60084b6fe2b0297a14493289c4f7ee88ae374ec518237ca6b13d39e7ae |
| MD5 | f91161c95cf32357b2b23b01ca4041c9 |
| BLAKE2-256 | 443e20fea85cf3b7054cd90da868b50640e9dc532509567462e623ea1aeefb42 |

